______ Are Systems Of Electronics
gruxtre
Sep 08, 2025 · 7 min read
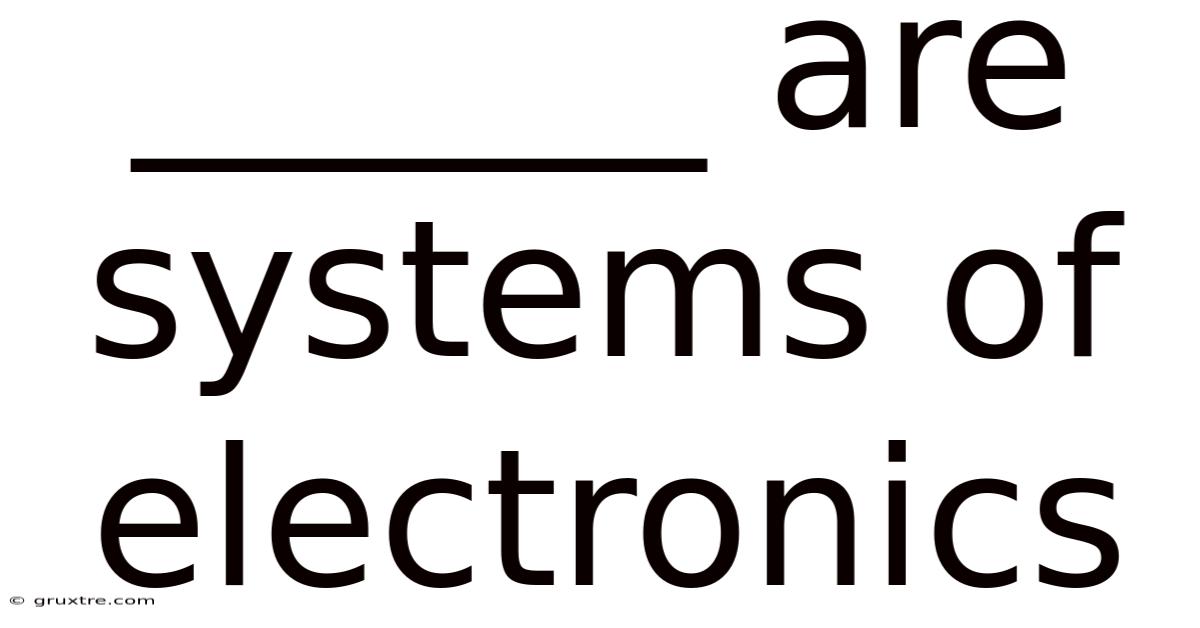
Table of Contents
Computers: Systems of Electronics That Revolutionized the World
Computers are systems of electronics that have fundamentally reshaped modern society. From the simplest smartphone to the most powerful supercomputers, they represent a remarkable evolution in electronic technology, impacting nearly every facet of our lives. Understanding computers as systems requires examining their intricate components, their underlying logic, and their profound influence on various fields. This article delves into the core principles of computers as electronic systems, exploring their history, architecture, operation, and the broader implications of their existence.
Introduction: A Brief History of Computing
The journey of the computer began long before the sleek devices we know today. Early calculating devices, like the abacus, provided a rudimentary foundation. Mechanical calculators, such as the Pascaline and the Difference Engine, marked significant advancements in automated calculation. However, the true dawn of the electronic computer arrived in the mid-20th century with the invention of the vacuum tube. These early computers, like ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer), were enormous, consuming vast amounts of power and generating significant heat. The development of the transistor in the late 1940s revolutionized the field, leading to smaller, faster, and more energy-efficient machines. The invention of the integrated circuit (IC), or microchip, in the 1950s and 60s further miniaturized components, paving the way for the personal computer revolution.
The Architecture of a Computer System
At its heart, a computer is a complex system comprised of several interconnected components. These components work in concert to execute instructions and process information. The fundamental architecture of a computer system can be broadly described using the von Neumann architecture, which emphasizes the central role of the central processing unit (CPU) and the memory unit.
-
Central Processing Unit (CPU): Often called the "brain" of the computer, the CPU is responsible for executing instructions. It fetches instructions from memory, decodes them, and performs the necessary operations. The CPU typically contains an Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) that performs arithmetic and logical operations, and a Control Unit (CU) that coordinates the activities of the CPU. Modern CPUs are incredibly complex, incorporating multiple cores and advanced features to enhance performance.
-
Memory (RAM and ROM): Random Access Memory (RAM) is volatile memory; it stores data and instructions that the CPU needs to access quickly. Data stored in RAM is lost when the power is turned off. Read-Only Memory (ROM), on the other hand, is non-volatile; it stores permanent instructions crucial for the computer's basic operation, such as the BIOS (Basic Input/Output System).
-
Storage Devices: These devices provide long-term storage for data and software. Examples include hard disk drives (HDDs), solid-state drives (SSDs), and flash drives. Unlike RAM, data remains stored even when the power is off.
-
Input/Output (I/O) Devices: These devices enable interaction with the computer. Input devices like keyboards, mice, and scanners allow users to enter data and instructions. Output devices like monitors, printers, and speakers display or convey the results of computations.
-
Motherboard: This is the central printed circuit board (PCB) that connects all the components of the computer system. It provides pathways for data and power to flow between different parts.
-
Power Supply: This supplies the electrical power needed to operate the computer system.
How Computers Process Information: The Role of Binary Code
Computers fundamentally operate using binary code. This means they represent information using only two digits: 0 and 1. These digits correspond to the presence or absence of an electrical signal, representing on or off states within the electronic circuits. Every instruction, piece of data, and character is translated into a sequence of binary digits (bits). Groups of bits form bytes, and bytes combine to represent larger units of information. This seemingly simple system allows computers to perform complex calculations and manipulate vast quantities of data.
The process of translating human-readable instructions into machine-readable binary code involves several steps. High-level programming languages, such as Python or Java, allow programmers to write code in a relatively human-friendly format. Compilers or interpreters then translate this code into assembly language and ultimately into machine code – the binary instructions that the CPU understands and executes.
Different Types of Computer Systems
The term "computer" encompasses a broad range of devices, each with its own specialized capabilities and applications. Here are a few key examples:
-
Personal Computers (PCs): These are general-purpose computers designed for individual use. They come in various forms, including desktops and laptops.
-
Servers: These are powerful computers designed to provide services to multiple users or devices over a network. They are often used in data centers and manage resources like websites, databases, and email.
-
Supercomputers: These are the most powerful computers in existence, capable of handling extremely complex calculations and simulations. They are used in scientific research, weather forecasting, and other computationally intensive tasks.
-
Embedded Systems: These are computers embedded within other devices, controlling their operation. Examples include the microcontrollers in appliances, automobiles, and medical devices.
-
Mainframes: These are large, high-performance computers designed for centralized data processing and transaction processing in large organizations.
The Impact of Computers on Society
The influence of computers on society is undeniable. They have revolutionized numerous fields, including:
-
Science and Engineering: Computers are essential tools for scientific research, simulations, and modeling. They have enabled breakthroughs in various fields, from medicine and materials science to climate modeling and astronomy.
-
Business and Finance: Computers are integral to modern business operations, facilitating tasks like data management, financial analysis, and communication.
-
Healthcare: Computers play a crucial role in medical diagnosis, treatment planning, and research. They are used in imaging systems, patient monitoring, and electronic health records.
-
Education: Computers provide access to vast amounts of information and educational resources. They are used in online learning platforms, educational software, and research.
-
Communication: The internet and related technologies, which are built upon computer networks, have revolutionized communication, connecting people across geographical boundaries.
-
Entertainment: Computers are used to create and enjoy various forms of entertainment, including video games, movies, and music.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: How does a computer store data?
A: Computers store data using various methods, depending on the type of storage. RAM stores data using transistors that can be switched on or off, representing 0s and 1s. Hard drives store data magnetically, while SSDs use electrical charges.
Q: What is the difference between software and hardware?
A: Hardware refers to the physical components of a computer, such as the CPU, memory, and storage devices. Software refers to the programs and instructions that tell the hardware what to do.
Q: What is an operating system?
A: An operating system (OS) is a software program that manages all the hardware and software resources of a computer. It provides a platform for other applications to run.
Q: How do computers work with images and sounds?
A: Images and sounds are represented digitally as sequences of bits. Images are broken down into pixels, each represented by a set of binary values that define its color. Sounds are sampled at regular intervals, and each sample is converted into a binary representation of its amplitude.
Q: What is the future of computing?
A: The future of computing is likely to involve even more powerful and efficient computers, along with advances in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and quantum computing. These advancements will have a profound impact on various aspects of life.
Conclusion: The Ever-Evolving World of Computing
Computers, as intricate systems of electronics, have fundamentally transformed our world. From their humble beginnings as large, power-hungry machines to the ubiquitous devices we carry in our pockets, their evolution has been remarkable. Understanding their architecture, operation, and broader societal impact is crucial for navigating the increasingly digital landscape. As technology continues to advance at an unprecedented rate, the future of computing promises even greater innovation and transformative potential. The journey from the abacus to the quantum computer is a testament to human ingenuity and the relentless pursuit of technological advancement. This ongoing evolution underscores the significance of understanding computers not simply as tools, but as sophisticated systems that shape our lives in profound and ever-changing ways.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
2024 Ahip Test Answers Pdf
Sep 09, 2025
-
Chapter 3 Anatomy And Physiology
Sep 09, 2025
-
Security Cooperation Activities Include
Sep 09, 2025
-
Tina Jones Musculoskeletal Shadow Health
Sep 09, 2025
-
Cats And Dogs Passage Teas
Sep 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about ______ Are Systems Of Electronics . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.